Accessibility Testing
As a web developer, creating websites that are accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, is essential. Website accessibility refers to the practice of designing and developing websites that can be accessed and used by everyone, including people with disabilities. Here's what you need to know about website accessibility.
What is website accessibility?
Website accessibility means ensuring that your website can be used by people with a wide range of disabilities, including visual, auditory, physical, and cognitive disabilities. This involves designing and developing websites that are compatible with assistive technologies, such as screen readers, braille displays, and speech recognition software.
Some examples of accessibility features that should be included on a website are alternative text for images, captions for videos, proper color contrast, keyboard navigation, and proper heading structure. By implementing these features, web developers can ensure that their website is accessible to a wide range of users with different abilities.
Why does it matter?
Website accessibility matters because it promotes inclusivity and ensures that everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, can access and use your website. Accessible websites also benefit businesses by increasing their reach and customer base. By making your website accessible, you can reach a wider audience, including people with disabilities who may not have been able to access your website before.
Moreover, there are legal and ethical reasons why website accessibility matters. In many countries, including the United States, websites are required to be accessible under disability discrimination laws. Failure to comply with these laws can result in lawsuits, fines, and damage to your company's reputation.
How it's done
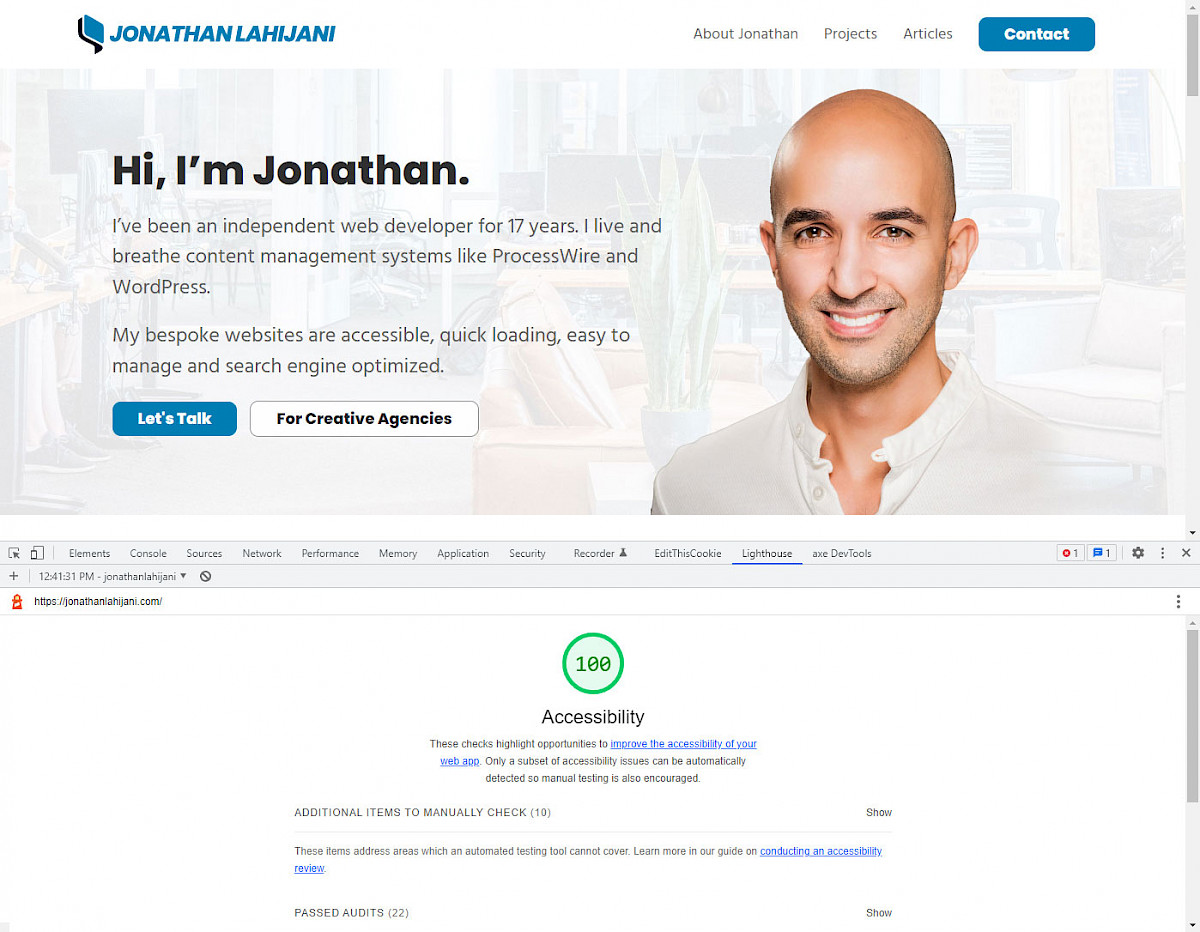
Web developers can make websites accessible by following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) created by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). These guidelines provide best practices for website accessibility, covering a wide range of topics, from text alternatives for non-text content to keyboard accessibility and beyond.
To ensure that your website is accessible, a web developer will use automated testing tools and make modifications to the code to correct any issues. Automated accessibility testing tools, such as Google Lighthouse, axe, WAVE, Accessibility Insights for Web, and SortSite can scan your website for common accessibility issues.
Why accessibility overlays should be avoided
Accessibility overlays, including products like AccessiBe, aim to automatically add accessibility features to websites without the need for manual coding or design changes. However, these overlays should be avoided as they are often ineffective, can create new accessibility issues, and can result in legal and financial risks. More information can be found on overlayfactsheet.com.
Instead, website owners should focus on manual accessibility improvements, including proper coding practices, testing with assistive technologies, and user feedback. By prioritizing accessibility testing and improvements, web developers can create websites that are accessible and inclusive for all users.
